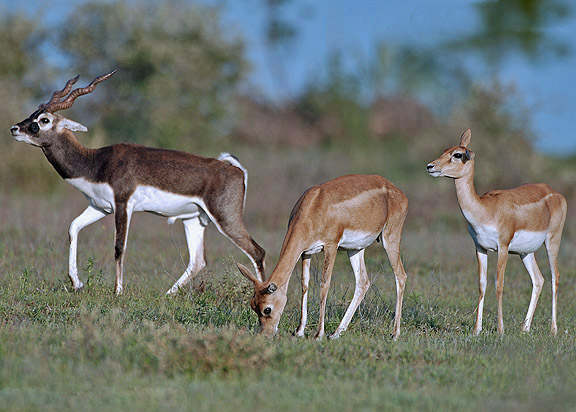
Antelopes, a diverse group of herbivorous mammals, exhibit a fascinating array of adaptations. One notable feature that varies among antelope species is the presence or absence of horns. This diversity sparks the question: Different ecological environments determine whether antelopes have horns or not
I. Horned Majesty: The Advantage in Open Landscapes
In wide-open grasslands and savannas, antelopes with horns often thrive. These majestic appendages provide advantages in defense, competition for mates, and communication. In such expansive environments, where visibility is high, horns become an essential tool for asserting dominance and navigating the challenges of survival.
II. Hornless Grace: Adaptations in Dense Forests
Contrastingly, in densely vegetated environments like forests, some antelope species have evolved to be hornless. In these confined spaces, where maneuverability is crucial, the absence of horns reduces the risk of entanglement and aids in navigating through thick vegetation. Hornless antelopes display a graceful adaptation to their specific ecological niche.

III. Sexual Selection: The Role of Mating Dynamics
The presence or absence of horns in antelopes is often linked to sexual selection dynamics. In open landscapes, where competition for mates is fierce, horns contribute to a male’s attractiveness and dominance. However, in environments where visibility is limited, other traits may become more critical in mate selection, rendering horns less significant or even a hindrance.
IV. Resource Allocation: Balancing Survival and Reproduction
The decision to develop horns or not involves a delicate balance of resource allocation. In environments where the energy cost of growing and maintaining horns is outweighed by the benefits they confer, horned antelopes may dominate. Conversely, in resource-limited environments, hornless antelopes may thrive by channeling energy towards essential survival and reproduction.
V. Evolutionary Pressures: Shaping Antelope Diversity
The ecological environments in which antelopes reside exert powerful evolutionary pressures that shape their physical characteristics. Over time, natural selection favors traits that enhance an antelope’s ability to survive and reproduce in its specific habitat. This ongoing process results in the remarkable diversity observed among antelope species today.
VI.Conservation Implications: Understanding and Preserving Diversity
Understanding the connection between antelope horn development and ecological environments is crucial for conservation efforts. Preserving diverse habitats ensures that antelope species can continue to adapt and thrive, contributing to the overall biodiversity of ecosystems. Conservation initiatives that take into account the intricate relationship between antelopes and their environments play a pivotal role in maintaining the delicate balance of nature.
VII. A Symphony of Adaptations in Antelope Ecology
In the world of antelopes, the presence or absence of horns is a testament to the intricate dance between evolution and ecological environments. Whether horns serve as majestic symbols of dominance in open landscapes or antelopes gracefully navigate dense forests without them, each species embodies a unique adaptation shaped by the demands of its habitat. This symphony of adaptations highlights the resilience and diversity of antelopes, showcasing nature’s ability to craft intricate solutions to the challenges of survival.